Amino acids are organic compounds which have a considerable meaning for our organism, and primarily for our muscles.
- What are amino acids?
- Why are amino acids important?
- What are essential amino acids?
- Which amino acids are essential?
- Why are amino acids essential?
- Why are amino acids conditionally essential?
- Why are amino acids non-essential?
- Are amino acids proteins? Amino Acids vs proteins
- Can amino acids be converted to glucose?
- Can amino acids be stored as fat?
- Why is it worth supplementing amino acids?
- Amino Acids vs BCAA
- What to combine amino acids with?
- Amino Acids – BCAA ranking
Therefore, this is so important to reach for amino acid preparations of appropriate quality. Certainly, not everyone of us is aware of the present market offer of such preparations and therefore the vast majority of us decide to first do some research on the Internet in search of reliable rankings.
Many of them fulfill the most important parameter of our trust or at least make such an impression.
The ranking of best amino acids, which you will find below decidedly deserves special attention. The preparations mentioned in it constitute an absolute cutting edge of what the market has to offer in the category of amino acid products. What is an indisputable merit (and advantage over others) is the focus on only four preparation so that not to leave you with the feeling of unlimited choice, which as we know often is problematic – especially in the case of amino acids, which are the components of incredibly diverse preparations.
Before we present the four best amino acid sources on the market, we introduce a few words of description – what they are and why they are so important.
What are amino acids?
Amino acids are chemical compounds, both the ones that the organism is able to produce by itself and the ones that it cannot synthesize, constituting the essence of life. It is not by chance, that they are called “the organism’s bricks”, as they fulfill a range of very important and essential functions. Amino acids are so varied that they can affect both whole systems and particular cell organelles. Their task is not only to increase anabolism and decrease catabolism – the most recognizable processes among physically active people – but also the functions of transport, regeneration, cleansing, transmission, energy and producing metabolically active compounds.
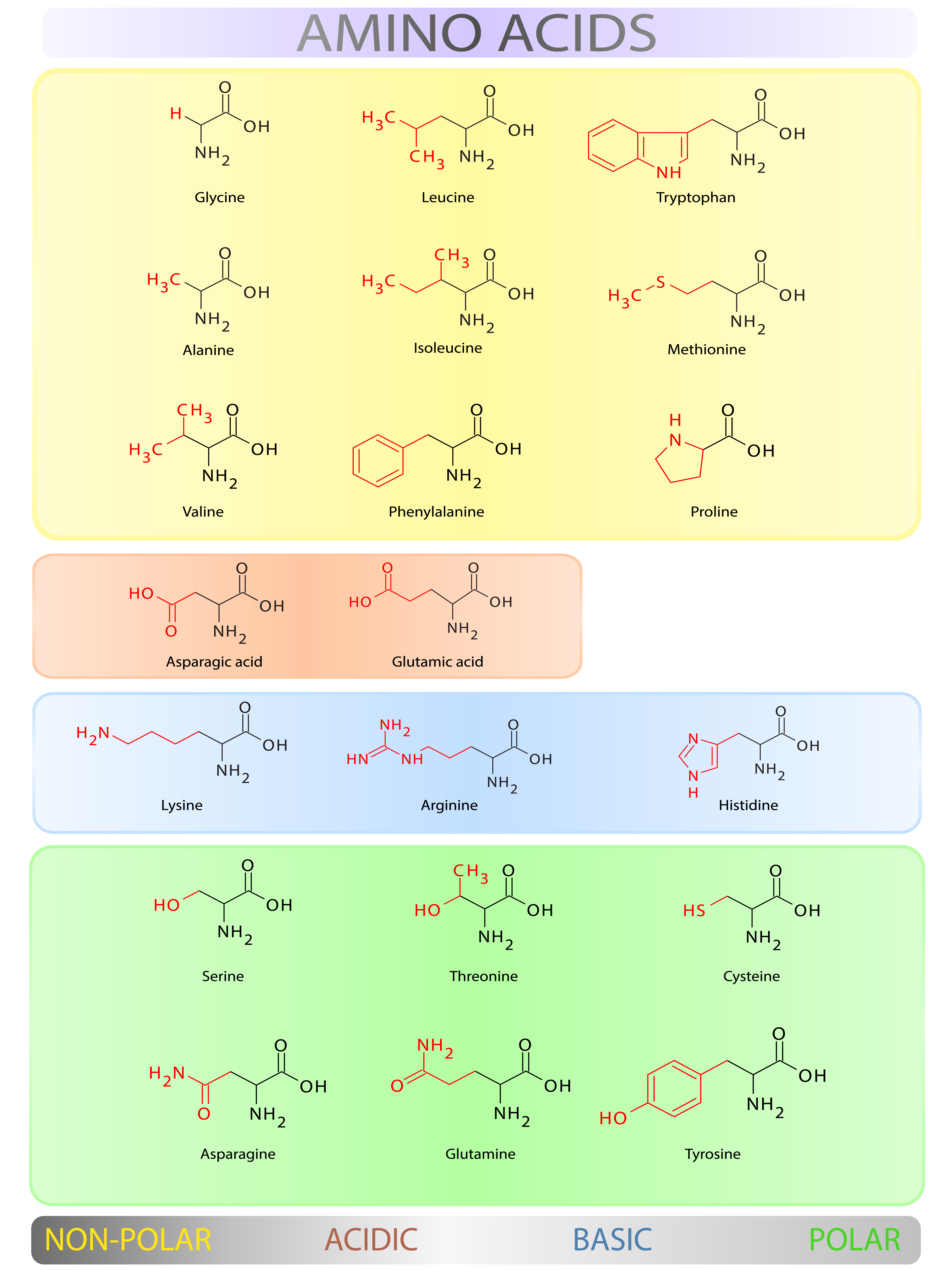
Why are amino acids important?
Amino acids are important because they are building brick of proteins inside our body. Without them, an organism cannot create proteins (by protein synthesis process) and proteins are crucial in our organism metabolism. Without they we wouldn't be able to live! Proteins are responsible for:
- Transport of substances throughout organism
- Immune system actions
- Energy metabolism
- Muscle synthesis
- Digestion processes
- Neurotransmitting
As you can see, proteins are the base of our organism actions. And amino acids, as building block of them are important for our optimal efficiency.
What are essential amino acids?
Essential Amino Acids (EAA) are amino acids, which cannot be synthesized by our organism, and they have to be included in our diet. That is also the reason why they are called exogenous amino acids - exo means "outside" from latin, which points its origin outside of our organism.
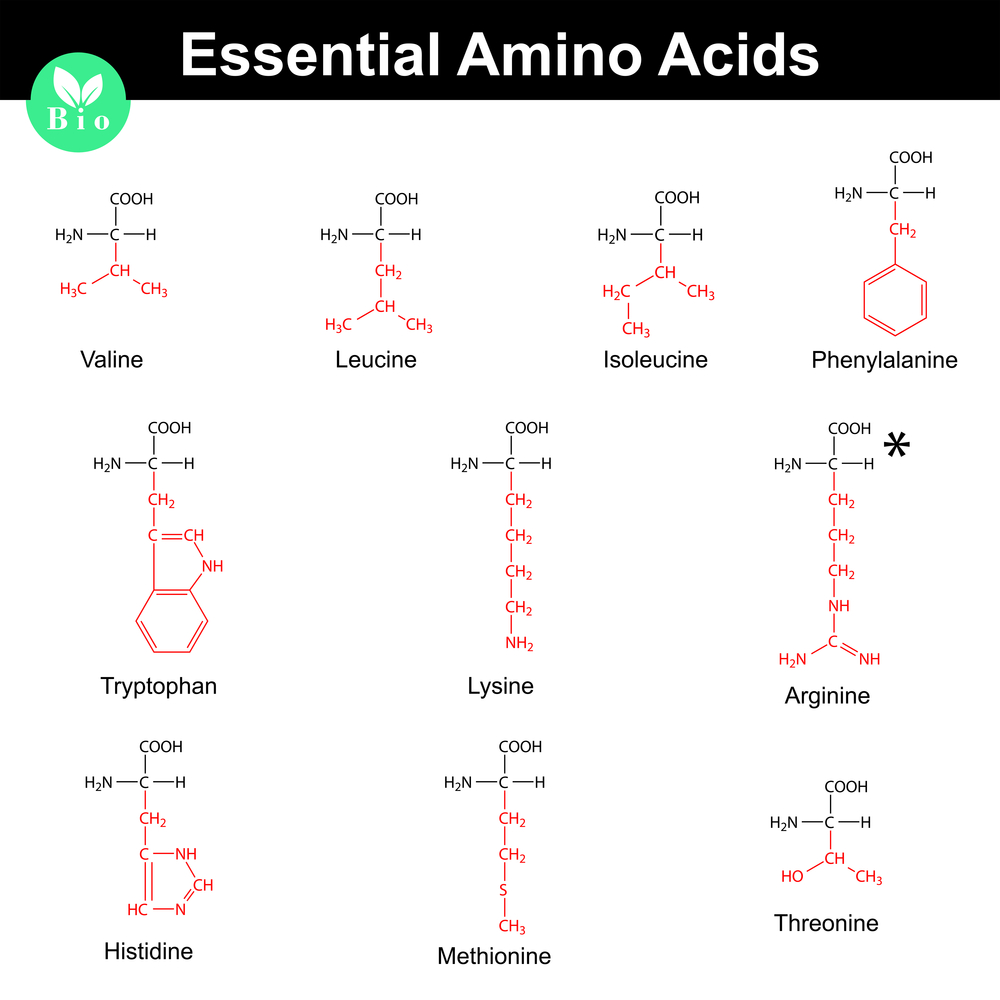
Which amino acids are essential?
There is 9 essential amino acids. Those are:
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Valine
- Histidine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
The first three of them are often called BCAA - Branched Chains Amino Acids, which points its specific structure. It has branched carbon side-chain, which cannot be made by our organism itself. We will talk about BCAA's more later in our article!
Why are amino acids essential?
Some of the amino acids are essential due to theirs speicifc structure. We can point three specific properties of structure to consider amino acid essential:
- an aromatic carbon part of side chain (Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Histidine)
- long side carbon chain (Lysine, Methionine)
- branched side carbon chain (Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Threonine)
Arginine is even more specific there, because even though it has long and branched side chain, it can be synthesized in urea cycle if there are deficiencies of it. So, if there is plenty of other amino acids, you shouldn't worry about arginine deficiencies. That is why arginine is considered conditionally essential amino acid.
Because they are essential we have to maintain theirs proper intake, or supplementation all the time.
Why are amino acids conditionally essential?
Conditionally essential amino acids, are:
- Proline
- Glycine
- Tyrosine
- Cysteine
- Glutamine
- Arginine
They are conditionally essential, because in normal conditions, in case of their deficiencies they can be synthesized from other amino acids in way showed below:
- Proline - through glutamate-5-kinase, glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase and pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase actions on L-glutamate amino acid
- Glycine - through 3-phosphoglycerate, serine hydroxymethyltransferase and glycine synthase actions on L-serine amino acid
- Tyrosine - through phenylalanine hydroxylase actions on L-phenylalanine amino acid
- Cysteine - through S-adenosylmethionine, cystathionine beta-synthase and cystathionine gamma-lyase actions on L-serine amino acid
- Glutamine - through enzyme glutamine synthetase actions on muscles proteins
- Arginine - through argininosuccinate synthetase and argininosuccinate lyase actions on L-proline and L-citrulline amino acids in urea cycle.
Nontheless, it is worth considering its supplementation, just in case. Better safe than sorry, isn't that true?
Why are amino acids non-essential?
In this group, we can specify:
- Serine
- Selenocysteine
- Pyrrolysine
- Glutamic acid
- Asparagine
- Aspartic acid
- Alanine
They are recognized as non-essential, because becasue they can be freely metabolised through other substances in our organism. So, their deficiencies are rarely seen. Nontheless, they can point specific diseases, so it is worth checking their intake and level in our organism regularly.
Are amino acids proteins? Amino Acids vs proteins
It is oftenly mentioned mental shortcut. Amino acids are not proteins itself, only a chain of them (at least 100 amino acids in chain linked by peptid bond through N and C ends) is called protein.
You can ask yourself "Wait, what if there is less amino acids in chain?". Well, we distinguish some types of peptides (chained amino acids):
- Oligopeptides - in case of chain with 2-20 amino acids. Oligo means "few" in latin, so you can guess why such a name was choosen
- Polypeptides - in case of chain of 21-100 amino acids. Sometimes, short proteins are also called polypeptides.
- Micopeptides - in case of chain of 101-150 amino caids. This name is sometimes used in exchange for small proteins.
Can amino acids be converted to glucose?
Such a questions arises mainly in the context of ketogenic or low-carb diets. If someone doesn't know already, a main reason of ketogenic diet is to make our organism prefer taking energy from fat metabolism (through ketone bodies) rather than from carbohydrates metabolism (which we are suited and accustomed to). That is why fat intake is highly increased, and carbohydrates are practically forbidden. One of the first questions is "Why shouldn't I eat that much proteins on ketogenic diet?". Because amino acids, can convert back to glucose if there is an excessive amount of them. What is important, a part of them must be converted to glucose to allow our brain to work properly. There are some nuisances which we cover in other articles.
Coming back - yes, amino-acids can be converted to glucose, if they are so-called glucogenic amino-acids. They are:
- Cysteine
- Glutamic acid
- Glutamine
- Glycine
- Aspartic acid
- Serine
- Valine
- Histidine
- Methionine
- Proline
- Alanine
- Arginine
- Asparagine
We can also distinguish amino acids which are both glucogenic and ketogenic:
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Tyrosine
- Phenylalanine
- Isoleucine
And those amino acids which are only ketogenic:
- Lysine
- Leucine
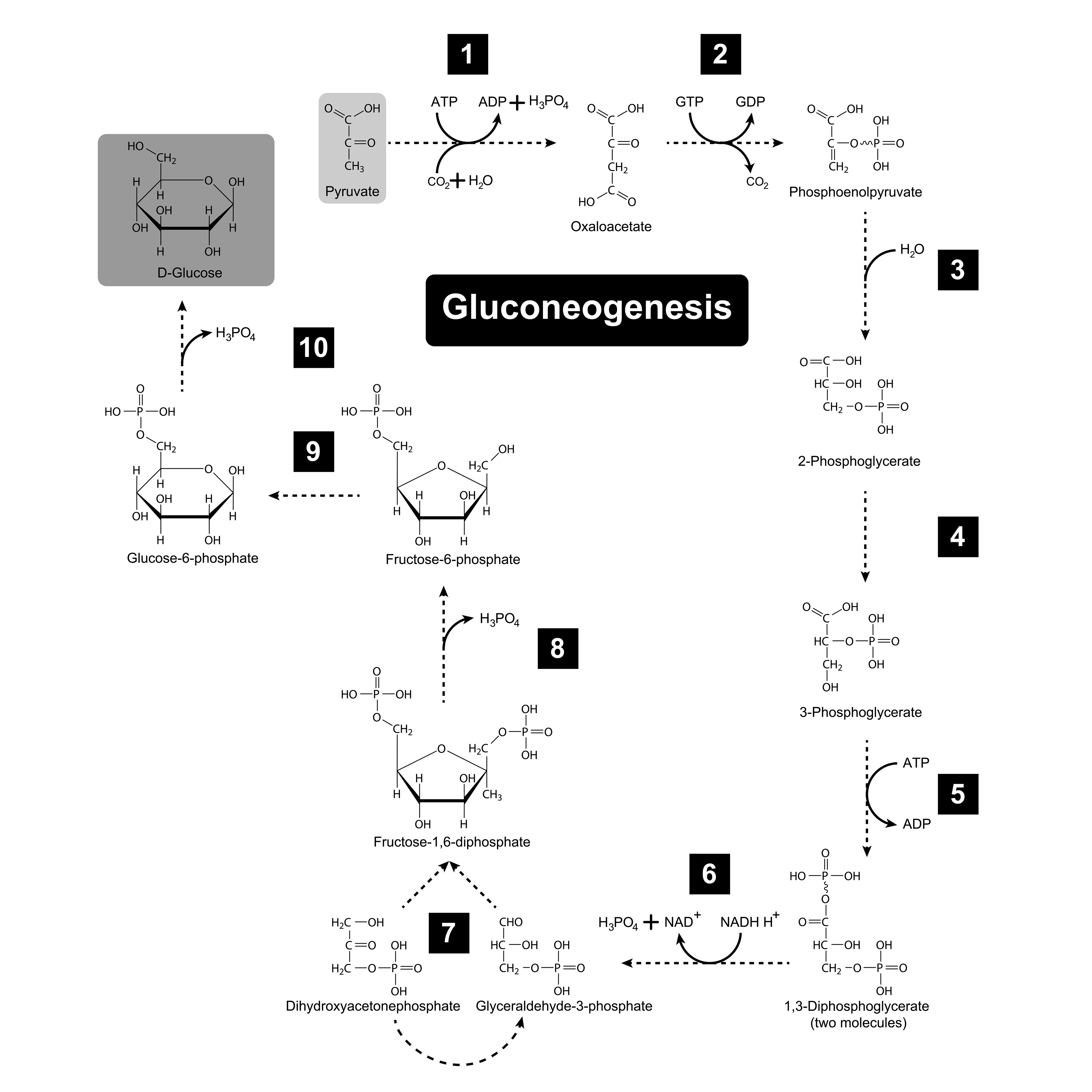
The first two groups of amino acids, can be converted back to glucose, in gluconeogenesis process (through converting them to alpha-keto acids [a pyruvate equivalent on the graph shown below] and then to glucose).
As you can see, there is no way to provide only ketogenic amino acids in case of ketogenic diet, and at the same time a high intake of amino acids (proteins) can increase gluconeogenesis rate, increasing a glucose level in our organism in result. That is why, in case of ketogenic diet is it recommended to maintain "proper" proteins intake, rather than its increase.
Can amino acids be stored as fat?
Every substance, which increase our caloric intake over caloric requirements in long time turns into fat finally. So, amino acids though they cannot be stored theirselfs in our organism, can be turned to fat through lipogenesis process. And that fat stay in our belly then!
Why is it worth supplementing amino acids?
Firstly, for safety of our organism. It's hard to track an intake of specific amino acids. Every protein source differs in its amino acids profile (a composition of amino acids in certain proteins), and it can be time-consuming to dig up and count every amino acid eaten. We would have to take in account a type of protein, its intake, digestion rate, our digestive tract state, and theirs interactions with other compounds in our food. So, we could say that there is no practical way to known our actual amino acids intake. Yet, we all know already how important their are for us.
What to do then? Take some amino acid supplement, and take worries of amino acids deficiencies from your head! It is that easy!
Secondly, every of amino acid have their specific benifical properties for our organism. For example:
- Leucine - improves muscle synthesis rate, and decrease catabolism rate
- Lysine - boosts immunity
- Glycine - improves brain efficiency and sleep quality
- Tyrosine - acts like stimulant and increase dopamine level
- Glutamine - improves regeneration
It's really hard to cover every of amino acids benefits there, but those shown above are oftenly the most commonly mentioned.
Amino Acids vs BCAA
BCAA is an acronym, forbranched-chain amino acids – a trio, which works out not only among sportsmen of strength disciplines, but also among people practicing endurance sports. They find application during the periods of building muscle mass, reducing fatty tissue, improving general efficiency of the organism as well as accelerating and improving regeneration processes. Valine, leucine and isoleucine constitute a huge resource of muscle tissue and they have strong scientific evidence confirming their precise effects.
What to combine amino acids with?
There is a variety of choices for synergistic supplementation of amino acids. We could suggest sets like:
Amino acids vs proteins
A proper amino acids set can improve a aminogram of concrete proteins source, compensating the limiting amino acid effect, which can lower bioavailability of proteins from that source.
Amino acids vs BCAA
If you supplement only BCAA's, then an addition of amino acid supplement, containing other amino acids (mainly essential ones) will allow you to gain more benefits from supplementation.
Amino acids vs creatine
There is no highly convincing reason to combine those two supplements, yet there is no reason to not to combine them! Creatine is always awesome choice of supplementation. And choosing supplement containing amino acid and creatine combination, will simplify your supplementation.
Amino acids vs pre-workout
Adding amino acids to pre-workout supplement (assuming, that pre-workout supplement doesn't contain amino acids at its own), will allow you to improve your training results. Amino acids are known for theirs endurance and strength improving properties, especially leucine. So it is worth combining those two together!
Amino Acids – BCAA ranking
Off The Chain from Hi-Tech Pharmaceuticals - probably the best amino acid supplement on the market!
urple Wraath from Controlled Labs - a full set of amino acids, with addition of endurance improving substances.
Go Pronto from Tim Muriello is innovative combination of BCAA and EAA, with addition of bromelain, which boosts amino acids bioavailability.
BCAA G-Force from Trec Nutrition - simple, yet good choice for BCAA and amino acids supplementation!





