heading_title
Posted By: Łukasz Szostko
Times Read: 4947
Comments: 0
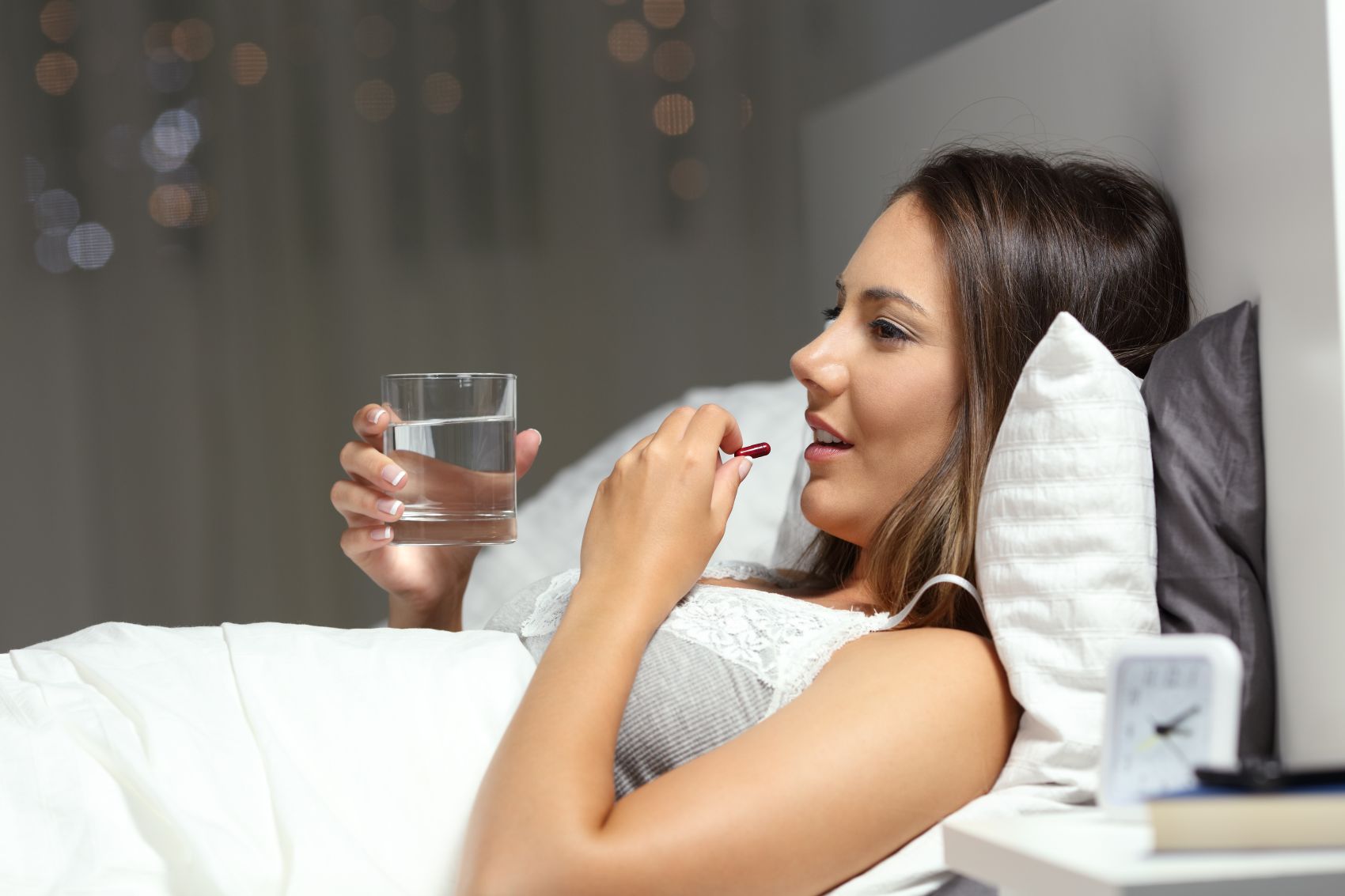
Melatonin tablets are a very popular way to improve sleep quality. However, sleeping aids usually do not have a good reputation in terms of their effect on overall health. How about melatonin? In general, melatonin is considered a very safe substance with a negligible risk of side effects. However, ...
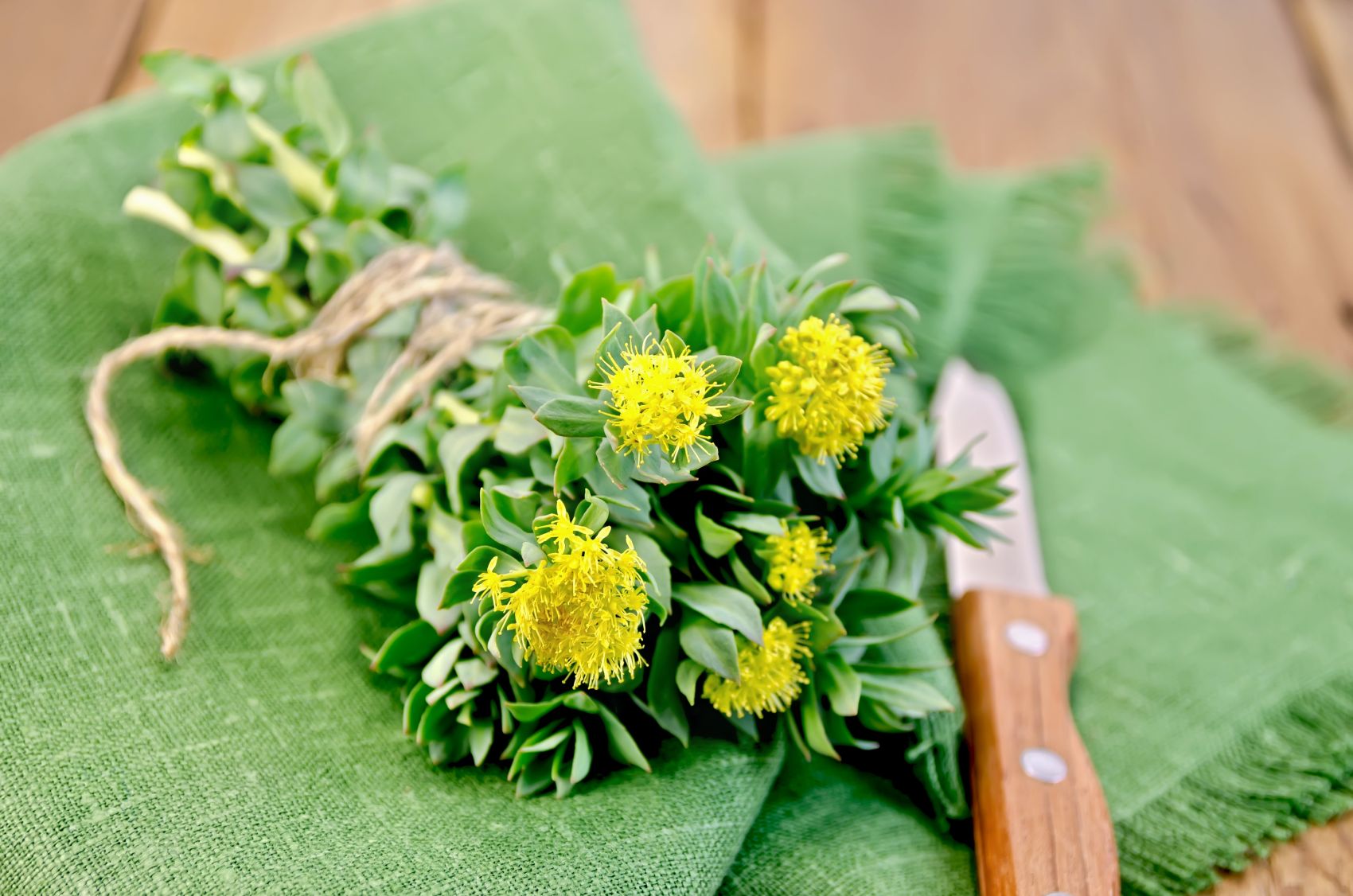

Rhodiola: supplementation, properties
17
Oct
2024
Posted By: Łukasz Szostko
Times Read: 3820
Comments: 0
More energy and less fatigue without caffeine? Why not! In telegraphic terms, these are the effects expected from Rhodiola rosea supplementation. This Arctic root is known for its adaptogenic and body-strengthening properties on many levels. With regular supplementation, it reduces feelings of ...

Kanna and energy - what are the relationships?
17
Oct
2024
Posted By: Łukasz Szostko
Times Read: 3452
Comments: 0
Much in life depends on the efficiency of the mind. Education, income level, or just plain brilliance in everyday situations. We all want to support the mind and increase natural energy levels, but the current fast-paced and stressful life is not conducive to this. Procognitive supplementation is ...
Posted By: Łukasz Szostko
Times Read: 1631
Comments: 0
Sleep is essential for good health, but many people do not experience its full restorative properties. If you suffer from sleep problems or have difficulty getting enough quality sleep, you may want to consider supplements or herbs for better sleep.
[toc]
The best supplements and herbs for sleep ...
Posted By: Mateusz Durbas
Times Read: 1211
Comments: 0
The arrival of autumn is not only the beautiful colors of the leaves on the trees and the falling leaves, chestnuts and acorns from the trees, but also a time of frequent colds and flu-like infections in people. Many people then reach for a variety of dietary supplements to strengthen the body's ...
Showing 1 to 5 of 242 (49 Pages)