GABA supplements have been very popular for years. Recently, however, their effectiveness is strongly undermined, using arguments about the inability of the molecule to penetrate the blood-brain barrier. Do GABA supplements work? Does GABA get into the brain? And does he have to get there?
Maybe for starters, what is GABA?
Under this abbreviation is the concept of gamma-aminobutyric acid. This is the main neurotransmitter inhibiting the function of our nervous system. It means that it has a soothing and calming effect, it relaxes the muscles and puts it to sleep. It is produced from glutamic acid by an enzymatic reaction using glutamic acid decarboxylase and can then be re-converted to glutamic acid. Together with glutamate, they maintain a proper balance of nervous system activity.
Why GABA supplements do not work?
In the first fire, let's take the most cited argument that the neurotransmitter's molecule is not able to pass from the bloodstream to the brain. It is true that under normal circumstances GABA transport to the brain is quite difficult. However, discussions on this subject are often mentioned in the work of your Kuriyama and Sze , where the impermeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) was found for GABA, But substance identical to GABA wasn't used. That one one had an additional OH4 group. To some extent, this disrupts credibility. In contrast, Japanese scientists, by studying the mouse brain, localized in the BBB tissue the GABA14 transporter molecule. Another report that may interfere with the interpretation of experimental results in the subject of BBB gamma-aminobutyric acid level is the fact that the migration of this neurotransmitter from the brain into the bloodstream is 16 times more intense than in the other side [16]. This makes the BBB not just a barrier, but rather a pump that protects the brain against excess GABA.
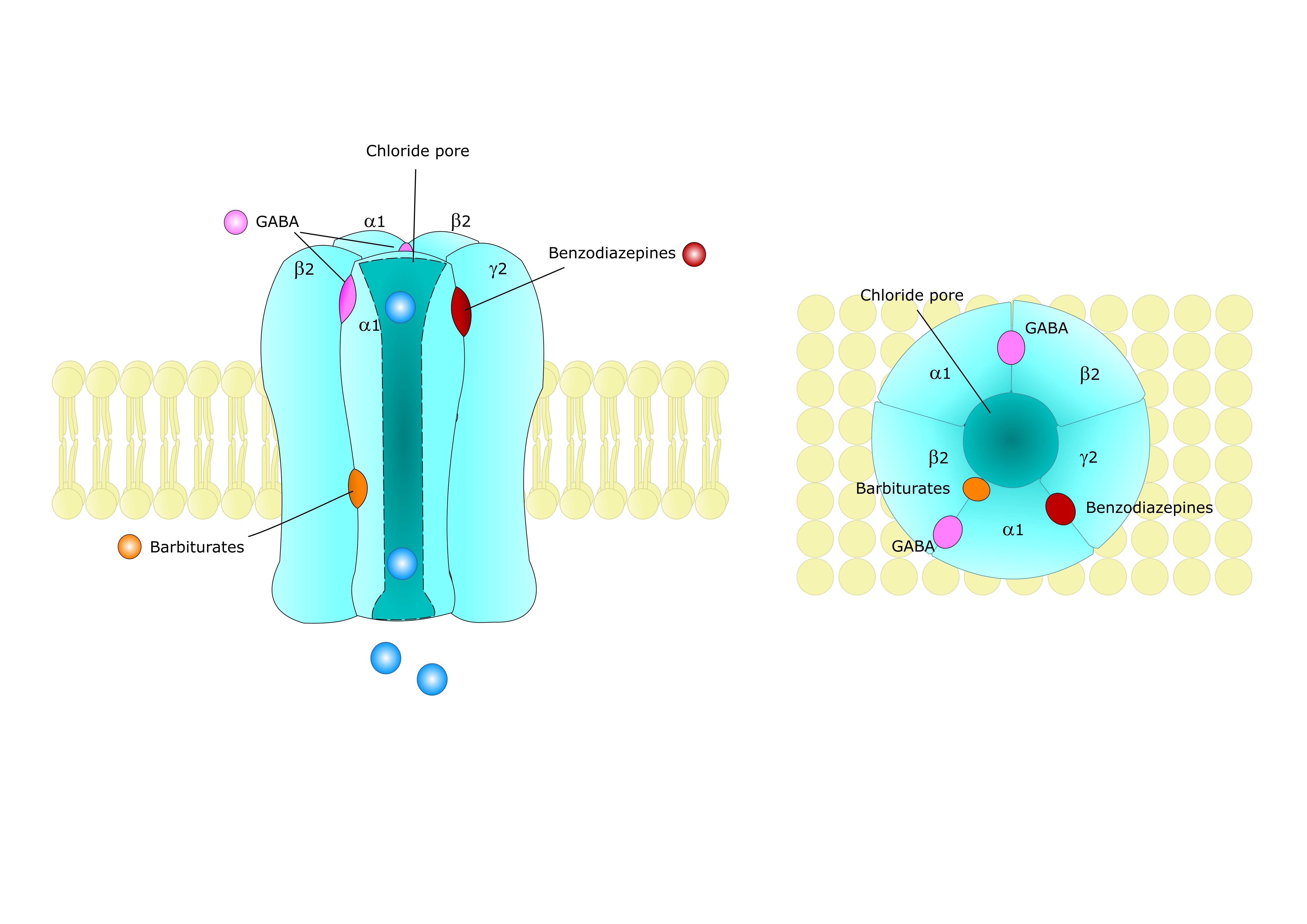
It is worth noting that the permeability of the blood-brain barrier is not constant. This parameter varies under different conditions, and in the case of GABA, the permeability increases considerably, for example, when nitric oxide increases, among others in response to an increased supply of arginine. Interestingly, in rats experiments, it has been observed that the administration of arginine alone causes a greater increase in GABA in the brain than the administration of this neurotransmitter directly. In contrast, the combination of GABA and arginine gave more than a 10-fold increase in the neurotransmitter in the brain, compared to the treatment with GABA1 alone. Other data suggest that nitric oxide is involved in the blocking of GABA transaminase (GABA-T), which means that more GABA remains in synapses2. This somewhat distorts the image of the previous study, because we see that not all of the arginine effect resulted from easier transport, but the part is due to the slower decay of the neurotransmitter. From yet other data, we can learn that nitric oxide enhances the action of GABA (A) 3 receptors. The GABA dose is also important, and more is not necessarily better. Transportation of GABA by BBB undergoes self-regulation - the more GABA we deliver, the more transport is inhibited. This effect may reach up to 80% inhibition5. Substances such as betaine, beta-alanine and taurine can inhibit the uptake of gamma-aminobutyric acid into BBB[14]. Beta-alanine also inhibits GABA absorption at gut level [12]. Certain data also indicate a decrease in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier with age17.
We already know that the unambiguous statement whether a GABA supplements work or not is impossible, because the effects are influenced by many other factors than just the dose used.
Let's take a look now at what effects have been noted in studies using GABA supplements.
One of the reasons why athletes reach for gamma-aminobutyric acid is growth hormone growth. As it turns out, you can actually record higher levels of this hormone as a result of supplementation. In the study on trained men, it was checked how GABA works at rest and how it works in conjunction with strength training, compared to training without supplementation. It turned out that delivery of 3 g GABA at rest gave a 400% increase in GH compared to placebo (3 g sucrose ). GABA in combination with resistance training resulted in a 200% higher concentration of growth hormone than in the case of placebo[6].
Extremely often, GABA is chosen when the goal is to fall asleep faster and improve the quality of sleep. Here, also beneficial effects were noted. And at a dose of just 100 mg! It is clear, therefore, that we use this supplement quite extensively because the dosage per capsule is usually in the 250-750 mg range. However, what exactly was noted? Thus, the results observed a shorter time of falling asleep faster time in deep sleep, prolongation of non-REM sleep stages, arousals, and a lower incidence of improving sleep efficiency. Subjective reports of respondents also indicated improvement, and comparing the results of PSQI questionnaires, we can see that the satisfaction with sleep increased and improved the feelings in the morning[7]. In the mouse study, it was also noted that GABA can neutralize caffeine-induced sleep disorders[9].
Reducing stress and anxiety is another reason why GABA supplements owe their popularity. The studies showed that one hour after admission, GABA increases the intensity of alpha waves in the brain and reduces the intensity of beta waves, and this effect is more pronounced than in the case of the famous theanine18. This shows that GABA supplementation affects the activity of the central nervous system and has an anxiolytic effect . In addition, it also improves the reactivity of the immune system to stress stimuli. In another study it was checked how a piece of chocolate enriched with GABA (compared to identical chocolate without GABA) will affect the behavior of the heart rhythm during the immediate psychological stress, which was the performance of the arithmetic task. The chocolate in the control group contained a small amount of GABA, because only 28 mg.
When analyzing the results of the electrocardiogram, it was noted that GABA allowed for a faster return to normal heart rhythm than placebo [19] chocolate. There is one more study in which people were given before a stressful situation (also an arithmetic task) drinks containing 0, 25 or 50 mg of GABA, respectively. Here, it was shown that 50 mg of GABA limits the psychological fatigue experienced after a stressful situation. Lower concentrations of cortisol and chromogranin A were also observed in the saliva of people who took 25 and 50 mg of GABA [20]. Chromogranin A ( CgA ) is a marker of psychological stress used in this type of research.
Now is the time to ask yourself an important question.
Does GABA actually have to cross the blood-brain barrier to produce effects?
It is known that GABA receptors are located not only in the central nervous system, but also in peripheral tissues, such as the intestines, lungs, blood vessels, bladder, heart, liver, thyroid, adrenals, pancreas and others [8]. Already on this basis, it can be concluded that certain actions of GABA already occur after getting into the bloodstream, before it reaches the brain.
Pharmacokinetic analyzes of GABA indicate that the peak concentration in the bloodstream after a dose of 200 mg is reached approximately 30 minutes after oral intake and then gradually decreases[7].In another publication, where a dose of 2000 mg was used, it was noticed that the peak level occurs between 60 and 90 minutes, and the half-life is about 5 hours. With regular use, the concentration does not accumulate[10].
Thus, when analyzing the peripheral effects of GABA, one can come across the mention of the regenerating properties of pancreatic cells, which is particularly attractive for type I diabetics. The action of this neurotransmitter in the pancreas is based on the intensification of β- cell replication and inhibition of their apoptosis. In the study of 12 relatively healthy participants, the effects of a single dose of 2 g GABA and dosing 3 times a day for 2 g for 7 days on glycemic parameters were checked . The results showed an increase in the production of insulin and glucagon, but without a significant effect on the level of glucose in the blood. A decrease in the level of glycated albumin was also noted along with subsequent study days10. Glycated albumin is a parameter used to determine glucose levels with a shorter period than the A1C and in situations where the A1C measurements seem to be insignificant [11]. Therefore, it can be concluded that orally administered GABA affects the regulation of glycaemia and has an anti-diabetic effect , even without exceeding the BBB. These doses, however, were already quite high and some people recorded negative effects. Among them, the most common are pain and burning in the throat, burning of the skin, pain and dizziness.
Another interesting issue is the action of GABA already at the intestinal level. Gamma-aminobutyric acid is produced, for good reason, by intestinal bacteria21, because it has quite a significant effect on the health and function of the digestive system. In the mouse study, it was noted that GABA increases the production of short-chain fatty acids (mainly acetate, propionate and butyrate ), which are the source of energy for the cells of the intestinal lining and allow them to mainta

in good condition. Other functions of these fatty acids are the prevention of the growth of pathogenic bacterial strains, the reduction of inflammation and the impact on the formation of bile acids in the intestine. The pH in the gut also decreased , which has a beneficial effect on the regulation of the bacterial flora13 . In particular GABA (B) receptors appear to be involved in interference with the condition of the digestive system 15. The agonism of these receptors is a potential target for the treatment of reflux , due to the effect of accelerating gastric emptying after meals. Activation of GABA (B) receptors reduces the release of acetylcholine in intestinal cells. Acetylcholine, by means of muscarinic receptors, intensifies peristaltic movements, so reducing its concentration may slow down intestinal motility.
We have a lot of speculation about the possibility of indirect influence of GABA on the functioning of CNS, without the need to transport it to the brain. Here you can refer to data on the effects of the microbiome and some probiotic strains on psychological functions. Many bacterial strains produce gamma-aminobutyric acid in the gut. It is possible that some anxiolytic actions of GABA are caused not by stimulation of the CNS, but by the nervous system located in the intestine, which causes an appropriate response via the vagus nerve [22].
GABA supplements - summary
There is a lot of data that indicates the effectiveness of GABA supplements in various aspects. There are also many premises questioning the arguments about the impossibility of a blood-brain barrier by GABA, because too many variables and unknowns can be found to provide a 100% sure verdict. However, if GABA gets into the brain or not, it does not define its effectiveness. Currently, there is growing interest in the peripheral action of this neurotransmitter and the topic of communication between the central and the intestinal nervous system, which is one of the potential mechanisms of action of supplements with gamma-aminobutyric acid. They have a lot of positive feedback and user relationships about effectiveness, so if the action is felt,it is possible, with a calm conscience, to ignore the controversial voices about the uselessness of orally accepted GABA. However, it is worth using knowledge about potential interactions, because some supplements may improve the action of GABA and others suppress them.






2 Comments