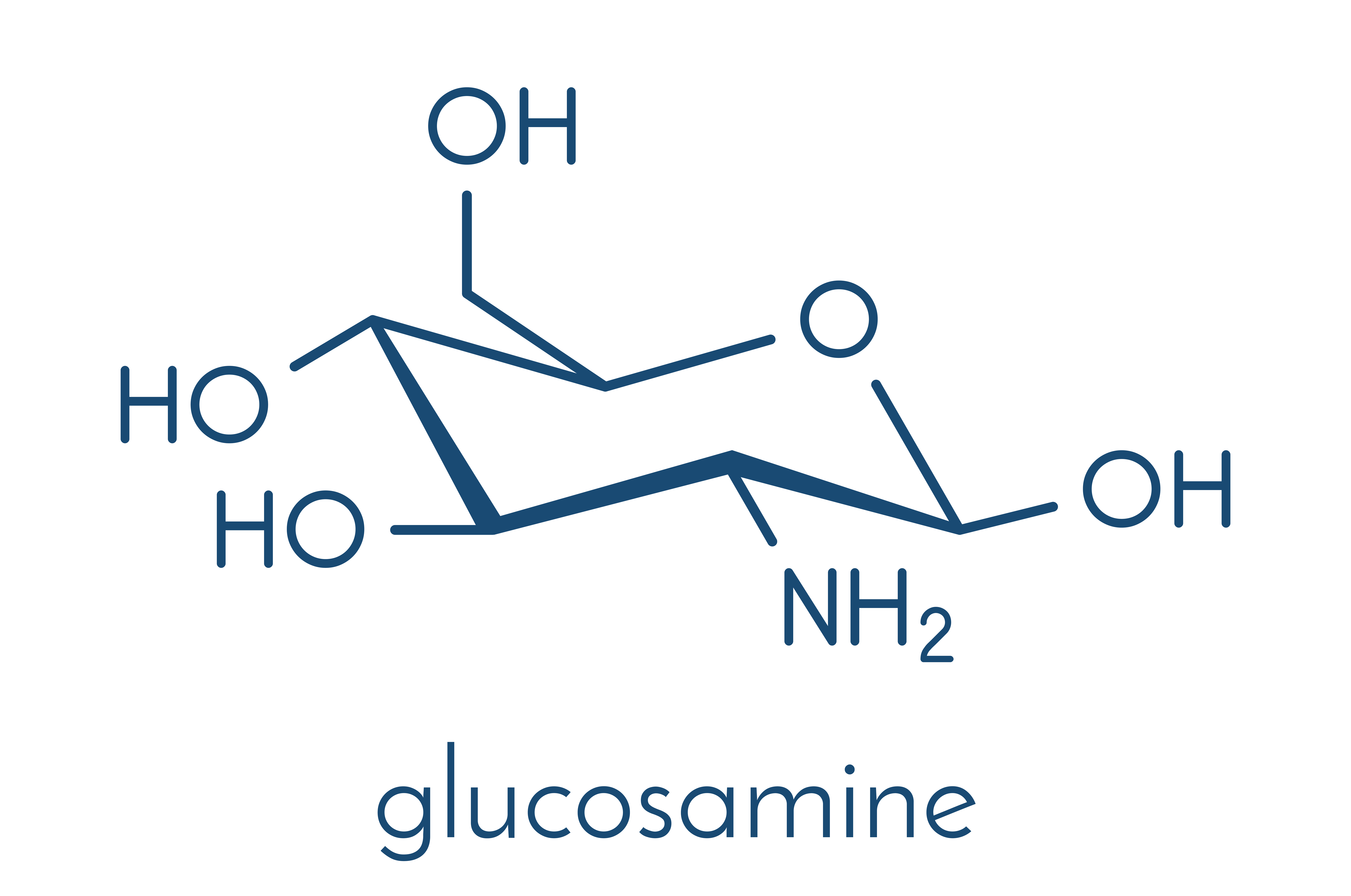
What is glucosamine
Glucosamine is the name of an aminosugin being an organic chemical compound, and also a glucose derivative. This supplement is naturally found in the human body and in crustaceans. In the human system, it can be found mainly in the cartilaginous and joint elements.
The most common forms of this compound are hydrochloride and glucosamine sulphate. In addition, forms in the form of hydroiodide are distinguishedand N-acetylglucosamine.
Glucosamine - action
The basic purpose of using glucosamine in systematic supplementation is regeneration of cartilage-joint elements in the body and reduction of pain caused by, among others, excessive strain or intense physical exercise. There is a very high probability of damage to joint joints due to excessive body weight, a diet low in calcium or any type of injury.
The above corrective activity of glucosamine depends on the mechanism of its action. This compound is responsible for the synthesis of proteoglycans, which are the basic building block of articular cartilage. The reduced content of these substances due to the above-mentioned reasons most often leads to pain during movement, reduced depreciation, increased susceptibility to injuries and deterioration of traffic quality.
It is also worth mentioning that glucosamine is a compound well tolerated by our body. The greatest therapeutic benefits are its use in the form of sulphate. This variation of glucosamine is characterized by the highest bioavailability, whereby almost 90% of the active substance reaches the bloodstream. This feature is used not only in sports supplementation, but also in medical treatment. Glucosamine sulphate is one of the main points of treatment for osteoarthritis and mineral defects, which results not only from injuries or injuries, but also from age or hormonal changes.
In conclusion, glucosamine supplementation is favored in:
- fighting pain and joint stiffness
- intensification of bone synthesis processes
- prevention of bone decalcification
- protection and strengthening of joint connections
- cartilage regeneration
- increasing flexibility and movability
Side effects of glucosamine
We mentioned above that glucosamine is a substance that is generally well tolerated by our body. This is true, however, as with most supplements, there is a risk of side effects. These symptoms most often result from abnormal supplementation with this preparation (using too high doses, exceeding the set standards) or allergy to seafood (most products containing this compound uses the shells of sea creatures). In addition, it is worth mentioning that diabetics should consult a doctor to include glucosamine in their supplementation, because this preparation favors changes in blood insulin levels.
The most common side effects in glucose supplementation are diarrhea, epigastric pain, bloating and constipation. Very often you can also note allergic reactions in the form of shortness of breath, erythema or pruritus of the skin.
Dosage of glucosamine
The daily dose of glucosamine should be between 900 and 1500 mg, and should be divided into three portions. The effectiveness of the product used depends on the dose taken. The supplement should be delivered to the body with a meal.
Opinions on glucosamine
In the scientific world, opinions on the effectiveness of glucosamine are divided. Below are some studies confirming and undermining the benefits of using this preparation.
The first test is a trial from 2004, when Cibere together with other scientists published the results of their research on a group of 137 patients. All participants suffered due to osteoarthritis of the knee joints and a month before the test they were taking glucosamine preparations. The research material was divided into two groups - control (66 - placebo) and research (71 - glucosamine). The result of this experiment was the lack of influence of glucosamine therapy on the reduction of osteoarthritis symptoms.
Reginster analysis from 2001 has different results. 212 volunteers took part in the study. For 3 years, they used a daily dose of 1500 mg of glucosamine and a placebo, and the experiment itself concerned the occurrence of changes in the articular cartilage. The consequence was to show a significant dependence - there was no structural deficiency in people using glucosamine.
Another example is the 2003 study, when Braham, Dawson and Goodman organized an analysis of the effectiveness of glucosamine supplementation
in a group of 46 people in the range from 20 to 70 years. The basic criterion for the selection of participants was the occurrence of pain in the knee joint. The research material was divided into two groups - 24 people took a daily dose of 2,000 mg of glucosamine, and the remaining 22 received a placebo. The whole test lasted 12 weeks, during which they did not perform any physical activity. The examined parameter was KPS (knee pain scale). The result of this study was a lower value of this indicator in people using glucosamine than in the control group. In addition, as many as 88% of patients from the research group declared feeling less pain.
The last study which I will quote is Hadki's work from 2012, when together with two other scholars, he conducted a study on the effectiveness of glucosamine in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. The research material consisted of as many as 215 volunteers who received a dose of 1500 mg of glucosamine sulphate within 24 hours. The trial itself was divided by control studies in which patients were monitored. The results of the study confirmed the effectiveness of using this supplement in the treatment of degenerative disease - in the case of pain in inclined walking the number of people reporting this symptom decreased by almost 75%, in the horizontal walk by less than 60%, and in the case of resting pain did not occur in 50% of respondents in relation to the initial number declaring the occurrence of this symptom.
What is chondroitin
Chondroitin is a chemical compound belonging to mucopolysaccharides. It consists of glucuronic acid residues and N-acetylgalactosamine. This substance is endogenous, so it is produced by our body. The main place of its occurrence is articular cartilage.
Preparations with chondroitin
The highest efficiency of chondroitin is noticeable in the form of sulphate. This relationship is very important due to the participation in eliminating the feeling of friction between articular surfaces. What's more, it naturally stimulates the body to produce synovial fluid, which is responsible for the proper functioning of the joints. Thanks to this, their structure is not destroyed, and the quality and mobility of the traffic is still at the right level.
A very popular solution is the combination of chondroitin with vitamin C. Thanks to this conglomerate, our body gets information about the increase in collagen production - a compound that determines the strength of our anatomical structures, such as ligaments or joint capsules, which are responsible for control and movement.
Chondroitin in food
As already mentioned - chondroitin is an endogenous compound, i.e. produced by our body on its own. However, continuous movement, resulting in permanent wear of the cartilage tissue causes that the quantity produced is too small, so that the daily demand for this preparation is completely covered.
Very often questions arise as to whether chondroitin can be delivered with natural food. Of course - it occurs mainly in the bovine cartilage and the curcuma. However, due to the limited availability of these products, it is more often recommended to take supplements with chondroitin in their composition.
Dosage
It is assumed that the daily dose of chondroitin-containing supplements varies from 0.5g to 4g. Very often we can encounter preparations that are specific conglomerates of three compounds chondroitin + glucosamine + vitamin C. This is a very good solution, because this combination determines a more comprehensive and holistic approach to protecting your own motor system, and also provides more effective protection against possible injuries.