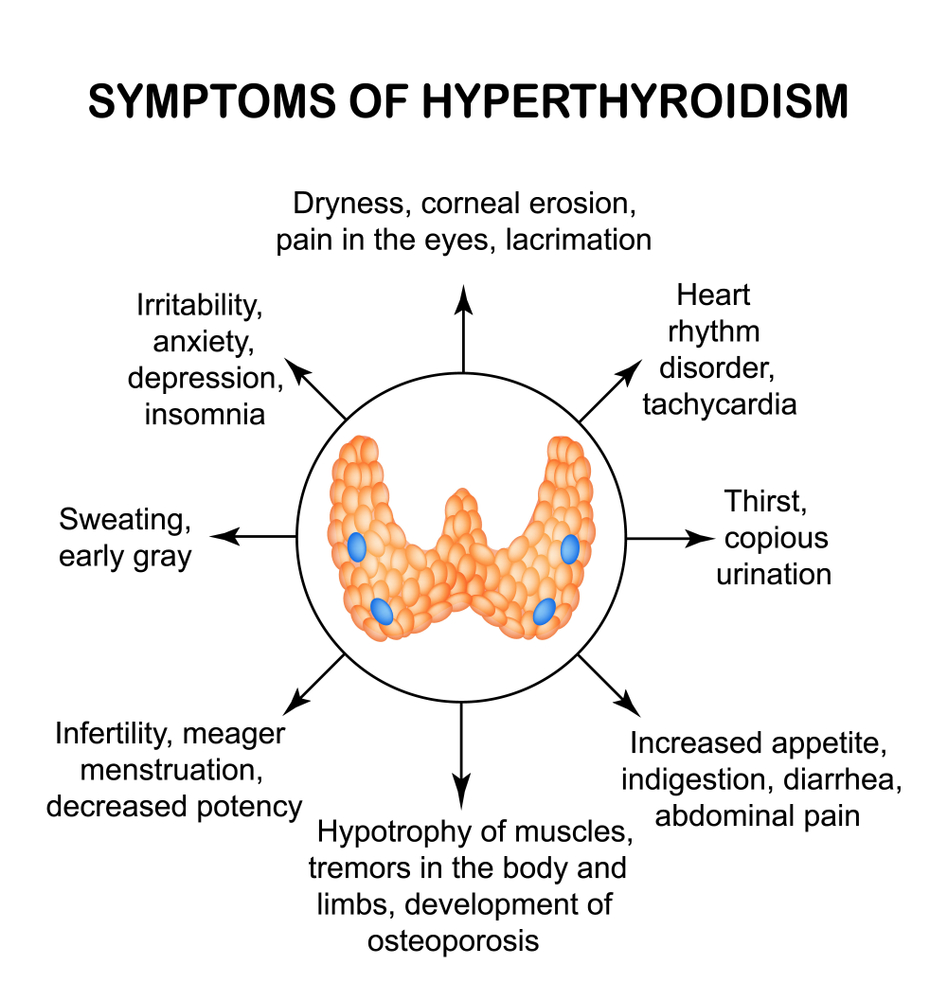
Hyperthyroidism is a condition of excessive thyroid hormone secretion. This term does not include the effects of excess thyroid hormones, which we term thyrotoxicosis. Untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to thyrotoxicosis. But also the administration of excessive amounts of thyroid hormone, which is used in hypothyroidism, can cause thyrotoxicosis (rather than hyperthyroidism, as often erroneously interpreted).
Hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis - causes
- Toxic nodules (producing hormones), more specifically, the presence of autonomic thyroid tissue (producing hormones without TSH stimulation)
- Thyroiditis (most commonly Graves-Based)
- Rarely, the hormone produced by the placenta during pregnancy
- Very rare pituitary disease and other diseases
At present, hyperthyroidism is increasingly seen in people with inert nodules who undergo the treatment of iodine-containing shots into toxic nodules. While this phenomenon can be considered as unavoidable (iodine-based or iodine contrast in imaging studies is not used for trivial reasons), it is unacceptable to be hyperthyroidism caused by "iodine treatment".
Detection
Hormonal studies - suspicion with TSH - confirmation by FT3.
Why so? So TSH is the most sensitive test, but its level is influenced by other factors than thyroid disease, so it does not determine the existence of the disease. (Here about abnormal results without thyroid disease) FT3 followed by FT4 followed by sensitivity, so it is better to use the first. Formerly preferred FT4 because of the lower price, today the price of both and so is small. At this point, it was time to pay tribute to my colleague Dr Jakub Swadźba, the builder of ‘Diagnostyka’, before which everything looked different - the prices were high, the research was not available and the idea of TRAb met with a shrug (in fact, it still does in Cracow).
Due to the sensitivity of the TSH test there is a concept of the so-called subclinical hyperthyroidism - TSH lowering without disturbing other hormones. Once it was confirmed by a TSH test, at present, this substance has been dramatically increased, the diagnosis of subclinical hyperthyroidism is confirmed by thyroid disease in USG and other causes of hypothyroidism are excluded.
After detecting hyperthyroidism, it is time to establish its cause - we perform an ultrasound scan and find:
- nodules
- Characteristics of inflammation
- Both
If we detect nodules - we need to know if these are excessive hormone (toxic) nodules or are inert (not producing excessive amounts of hormones) that are not associated with hyperthyroidism. For this we use scintigraphy - a study of iodine uptake by thyroid. Lumps capturing iodine more than the surrounding tissue is called "hot". If the USG shows signs of inflammation, we can confirm this by testing the aTPO or TRAb antibodies.
Treatment of hyperthyroidism
The treatment consists of:
- Inhibition of thyroid hormone production by the so-called thyrotoxic drugs - Metizol, (Thyrozol, Thiamazole), Propycil (thyrosan)
- Inhibition of thyroid hormone effects by beta-blockers (most often propranolol)
- Elimination of abnormal thyroid tissue
In thyroiditis there is a possibility of cure by using only pharmacological treatment - in Graves-Basedov disease we typically use them for one and a half years in initially large doses, then smaller. If the disease recurs, complications (such as eye symptoms) or medications cause side effects (unfortunately not so rare), and we have to eliminate abnormal thyroid tissue.
Toxic nodes after initial treatment need to be eliminated. Long-term treatment with thyroid hormones is unlikely - it is a request for complications, and in addition it can cause thyroid enlargement - these drugs inhibit hormone production, but the volume of the thyroid can increase.

Subclical hyperthermia is treated only in certain cases - e.g. pregnancy or cardiac arrhythmias. Currently, the appropriateness of the treatment of subclinical hyperthyroidism in older people is increasing. On the other hand, in these age groups, the incidence of NTIS (ESS) is increased in the NT-associated thyroid hormone level, which requires a particularly thoughtful decision to introduce treatment.
The management of hyperthyroidism in pregnancy is somewhat different, they are discussed in the article hyperthyroidism in pregnancy.
These drugs are currently preferred by Metizol (Thyrozole, Thiamazole). Its competitor Propycil (Thyrosan) is much more expensive and therefore for many years considered "better" (hereafter doctors treating only expensive medicines are considered "better"). Today we know that this is not the case, summa summarum this drug has more serious side effects; we use it only in certain cases where its positives outweigh the negatives (the first trimester of pregnancy, skin symptoms after metizol).
Methods of abnormal thyroid abnormalities are:
- Radioactive iodine treatment (J131 - radioiodine) - after oral administration, this agent is captured and destroyed by the thyroid gland
- Thyroid nodule destruction by ethanol injection - described in separate article ·
- Surgical removal of the thyroid (vasectomy)
Certificates for surgery and contrast studies
A patient with thyroid disease is often asked by other specialists to submit a certificate stating that there are no contraindications to the above activities. Why? Contrast with iodine content may result in patients with untreated hyperthyroidism exacerbation of symptoms and onset of complications (e.g. arrhythmias).
Similarly, during surgery, the condition of a patient with untreated hyperthyroidism may worsen dramatically until a life threatening complication known as hypermetabolic coma. Patients with hyperthyroidism (even subclinical, asymptomatic) should therefore have a thyroid medication in advance and surgery (if possible) should be delayed until FT4 is normalized.
Now we have to go back to the distinction between thyrotoxicosis and hyperthyroidism. Thyrotoxicosis, due to overdose of thyroid hypothyroidism, is not a contraindication for iodine contrast. It does not threaten the hyperthyroidism; after all, the patient does not suffer from this disease. When planning surgery, thyrotoxicosis is much less risky, usually with a correction of the drug and a short delay; you do not have to wait for TSH to be normalized, which is a test with significant "inertia."