The ketogenic diet is included in high-fat and low-carbohydrate diets. If you want to feel extremely light and feel great, turn off carbohydrates from your daily menu and replace them with fat. This method is used, among others in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy in children.
What's ketogenic diet?
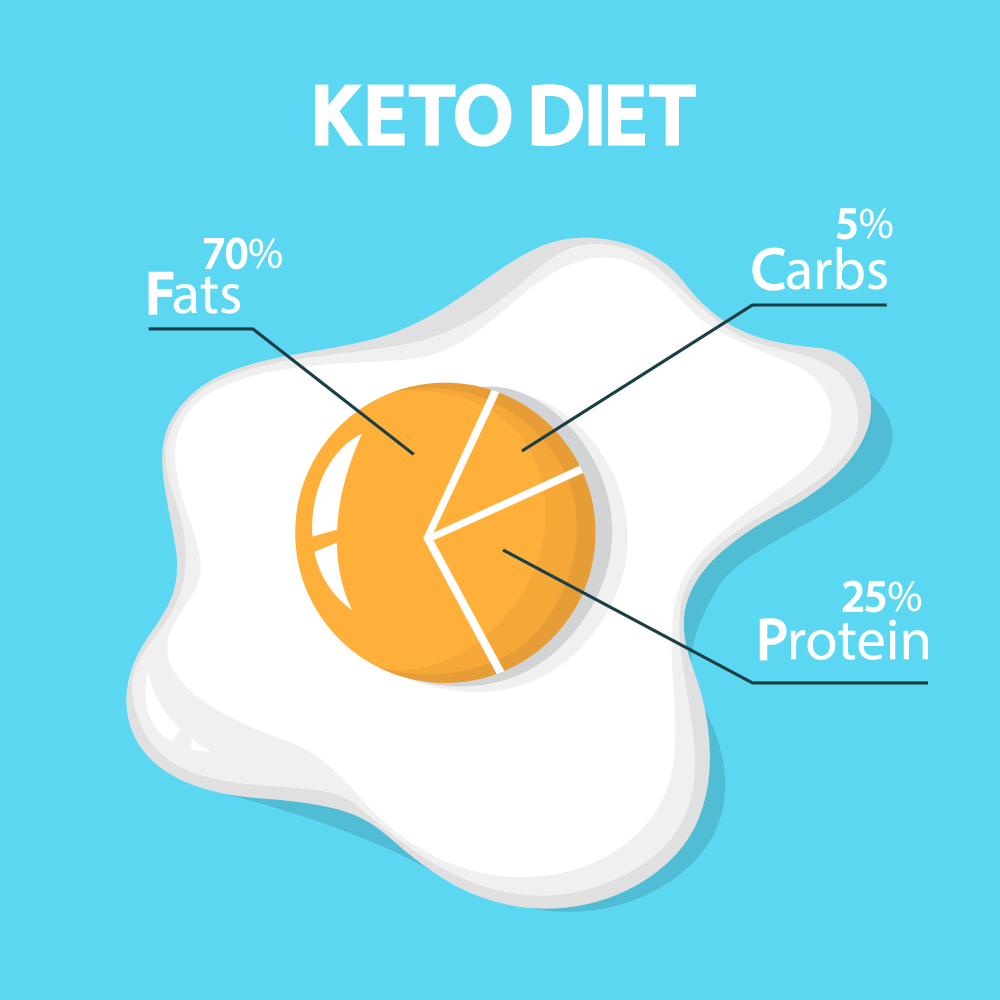
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat and low-carbohydrate diet. About 35 per cent is consumed in the daily diet. fats, 50% carbohydrates and 15% proteins. In the ketogenic diet, fat can constitute 80-90 per cent. of supplied energy, and the remaining 10-20% it’s a total of protein and carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy. When they are missing, the body begins to look for another fuel These are fats, specifically ketone bodies (so-called ketosis) formed in the process of fat breakdown. However, they provide orgasm only 70%. the energy needed, so it is malnourished. After a few days of using the ketogenic diet, a person enters a euphoric state (this is how doctors determine the effect of ketones) - they have excellent mood, are cheerful, light. After 2-3 months, everything passes. Appear loss of appetite, drowsiness and constipation, the smell of sweat, urine and breath changes, thirst increases.
Ketogenic (ketogenic) diet - indications
The ketogenic diet has found application in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy in children and in some congenital metabolic errors (e.g. congenital lack of GLUT-1 glucose transporting protein). There are also other indications for its use, such as Rett syndrome, Dravet syndrome, epilepsy with myoclonic seizures (Doose syndrome), and tuberous sclerosis. Therapy supporting ketogenic diets in autism, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, other types of epilepsy or some encephalopathies is also being considered.
Ketogenic (ketogenic) diet in an epilepsy
It has not yet been explained why the ketogenic diet reduces the frequency of seizures. High fat supply with a negligible amount of carbohydrates in the diet leads to changes in fat metabolism, similar to fasting. From the fat, ketone bodies in the liver form acetone, acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyric acid, which penetrate the central nervous system and constitute a substitute, in the absence of glucose, energy material for neurons. However, they are only indirectly responsible for the anticonvulsant effect. Ketone bodies are suspected
In addition, ketone bodies can protect nerve cells, including against damage from free radicals (they reduce oxidative stress).
The ketogenic diet - remember to supplement the deficiency of some vitamins
A ketogenic diet leads to a shortage of some nutrients. Therefore, when using it, remember to supplement preparations containing calcium, vitamin D, water-soluble vitamins and some trace elements.
Currently, several versions of the ketogenic diet stand out in the treatment of drug-resistant epilepsy
People with liver, kidney and pancreas disease and diabetes cannot use the ketogenic diet.
In a traditional ketogenic diet, a diet of 41 or 31 is generally used, i.e. 4 or 3 g of fat accounts for 1 g of protein and carbohydrates combined. Dietary fluids are limited to 60-66ml/kg/day. The diet begins in the hospital, under the control of a doctor and dietitian, preceded by starting it with 1-2-day fasting. Then gradually the amount of energy and nutrients administered increases up to the values determined according to diet assumptions. Further treatment is carried out at home and usually lasts 2-3 years. During this time, you must strictly follow the rules of the diet, because any deviation from the norm can promote epileptic seizures.
Ketogenic (ketogenic) diet for cancer?
Some argue that a ketogenic diet can be used to treat obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, chronic fatigue, hypertension and even cancer. However, specialists emphasize that there is no evidence confirming the effectiveness of the ketogenic diet in people struggling with malignant tumours. What’s more, switching to a ketogenic diet during cancer can result in complications due to the increased amount of metabolic products in the body.
Ketogenic (ketogenic) diet for slimming
During the ketogenic diet, the body does not draw energy from carbohydrates, but from consumed and own fats and protein, which is used by people who want to get rid of unnecessary kilograms. In addition, ketone bodies suppress hunger.
Ketogenic (ketogenic) diet - side effects
Adverse effects may occur during the ketogenic diet. At first, the patient may complain of constipation or diarrhoea, vomiting, abdominal pain, which usually disappear after the body adapts to the diet. The accompanying symptoms are fatigue, drowsiness, loss of appetite, and feeling thirsty.
With prolonged use of the ketogenic diet, urolithiasis and hyperuricemia (increased blood uric acid levels) may occur.






