Creatine is one of the few substances with anabolic effect that is available without a prescription! Its effectiveness in terms of anabolism is unquestionable - hence in building muscle mass and increasing muscle strength!
- What is creatine
- How does creatine work?
- How creatine is made
- Creatine contradictions
- Who should take creatine?
- Creatine and creatinine - what's the difference?
- Creatine and creatine kinase - are those things the same?
- When to take creatine?
- Creatine load and creatine cycle - are they worth the trouble?
- Is creatine safe?
- Is creatine worth using?
- Is creatine steroid?
- Creatine comprasions - what to combine creatine with?
- What is Creapure?
- Creatine forms - which one to choose?
- The best creatine
- We present the best creatine products on the market!
What is creatine
We have already written about creatine in the context of the most important substance for the development of muscle mass. It is worth mentioning this article by one of the active players in classic bodybuilding showing what supplementation looks like in this sport - of course there is a place for creatine in it.
Creatine is a substance orginally found in mammalian muscle tissue, especially in liver and kidneys. It takes part in creatine phosphate energetic system in our body. In short - creatine is a part of creatine phosphate compound. And this compound is directly responsible for regenerating the basic energy compound of our organism - ATP. A phosphate group is detached from creatine phosphate and it's atached to ADP, which in result turns to ATP back again.
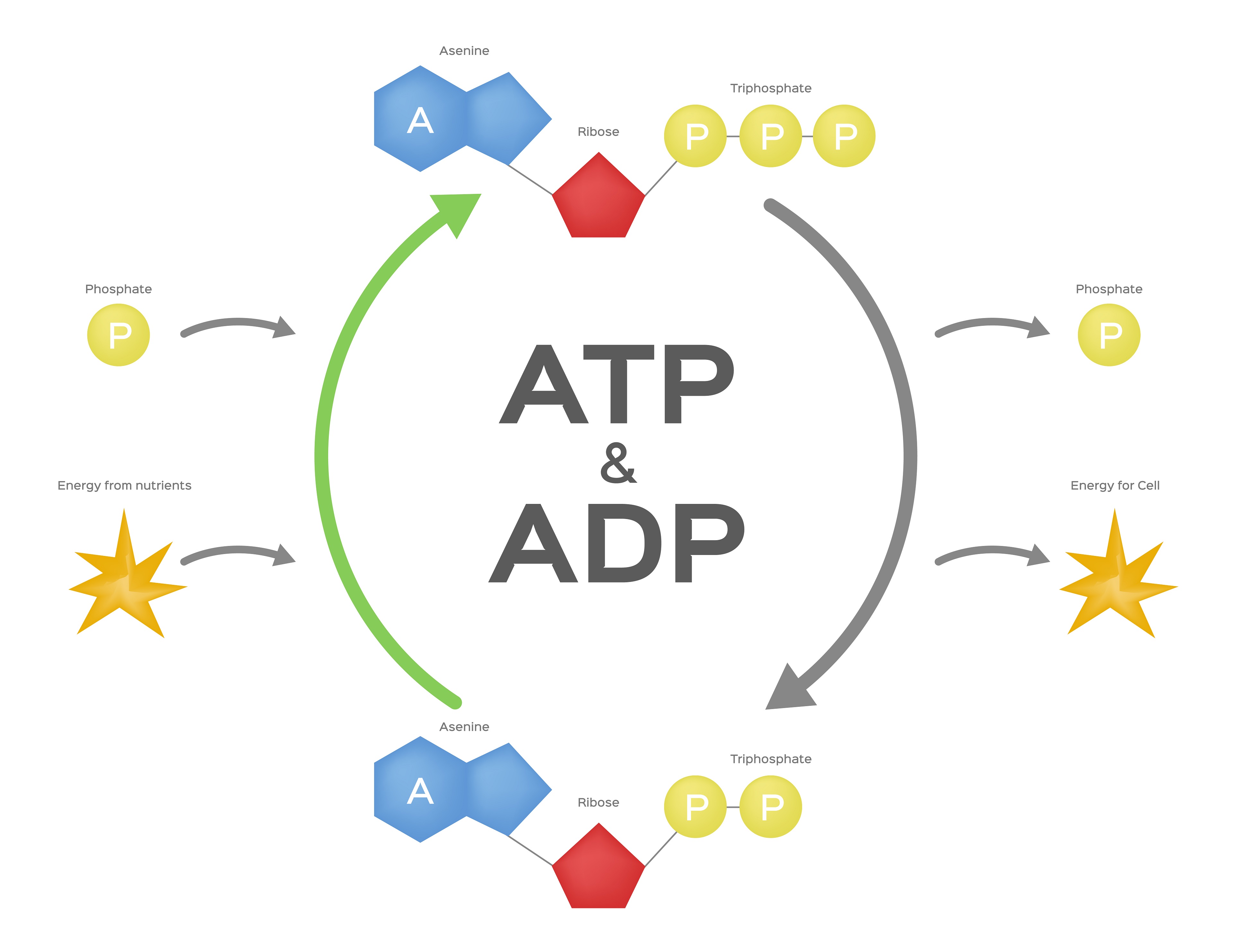
How does creatine work?
This you will learn from this article, as well as the difference between monohydrate and creatine malate. You will also find a lot of interesting information here. Wojciech Nowosada presented the alternative effect of creatine in a great way:
"Creatine interacts with serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT1A subtype, and the ability to improve the effects of SSRIs, such as sertraline, fluoxetine, paroxetine and citalopram, can be improved. Creatine supplementation may be due to creatine supplementation, but this depends on There are indications that women derive significantly more benefits in this field than men, the first of which is a rat study in which females have reduced anxiety and improved performance in the forced swimming test in response to creatine supply, indicating In males, similar efficacy has not been demonstrated in males. In women resistant to fluoxetine, the use of adjuvant therapy in the form of 4 g Creapure daily for 8 weeks gave a significant improvement, reducing the symptoms of depression by over 56%. in women using escitalopram in the company of 5 g creatine, obtaining a greater improvement than with escitalopram alone. "
How creatine is made
Here, we have to distinguish two things. How creatinine is made inside our body, and how creatine is done as supplement
Biosynthesis of creatine
In our organism, creatine is created by synthesis of glycine and L-arginine. Their complex - guanidinoacetate is then methylated by SAMe, creating creatine compound at its own. Then it's commonly phosphorylated by creatine kinase.
How is creatine produced at industry?
The most common way to produce creatine to put in your favourite, colorful cans with overpowered men, is the use of sarcosine and cyanamide. Sounds like poison? Actually, is the purest and most convenient method to produce large amount of creatine. From the synthesis of those two compound we are receiving a creatine compound.
Creatine contradictions
Will creatine make you fat?
Creatine will make you gain weight, that's true. But that's only water and definitely not fat!
Creatine increases a rate of water retention to your muscles, improving their environment to growth. What's actually more important is, that creatine actually can help you in losing fat, by increasing muscle mass, which burns more calories than any other type of tissue inside your body.
Will creatine make you bald?
Definitely not. Creatine actually is beneficial for hair and skin condition. That is why creatine is widely used in topical creams.
Can creatine cause acne?
It shouldn't. Creatine has interesting properties in terms of improving skin condition, by antioxidation and increasing a rate of collagen synthesis.
Can creatine cause bloating?
It depends on form of creatine. Creatine monohydrate, Creapure, or anhydrous form of creatine can cause some bloating,due to being hygroscopic (they are prone to absorb water from your digestive tract). It all can be dealt with appropriate amount of water drunk with creatine.
However, if bloating is still a problem even though you are drinking a lot of water with creatine, try more soluable form of creatine, like creatine malate or orotate.
Can creatine make you tired?
It cannot. The only tiredness symptoms, which are noticed is rather related to bloating effects of creatine (mentioned just before the moment), rather than to creatine properties.
Can creatine cause anxiety?
As before, creatine has nothing to do with anxiety. It's rather placebo effect, when you are trying some new supplements an thing that they are making you anxious. What's interesting, creatine can actually act as antidepressant through dopaminergic and serotonergic mechanisms.
Can creatine make you angry?
Again - getting angry after taking creatine is just placebo. Creatine has nothing to do with increasing adrenaline and related hormones level, which is the main reason of getting angry.
Can creatine cause headaches?
Creatine cannot cause headaches at its own. However, creatine supplementation is related to increased water intake demand of our organism. And here, if we don't drink additional amount of water, can make us dehydrate a little, which in result can cause headaches.
Who should take creatine?
The most common reply to this question is "everyone should". And that's no suprise! Creatine has so many benefits, that nearly everyone can benefit from its usage. The only real contradiction is extreme renal failure, in which excessive amount of creatine can be additional load for your kidneys.
Creatine and creatinine - what's the difference?
Creatinine is inactive metabolit of creatine, to which excessive creatine amount is metabolised inside our body, with the help of water.
Creatinine is also a reason why it's not recommended to dissolve creatine in water to drink it later. In such environment creatine is metabolised to creatinine and when we drink it later, we supplement worthless, nonactive substance.
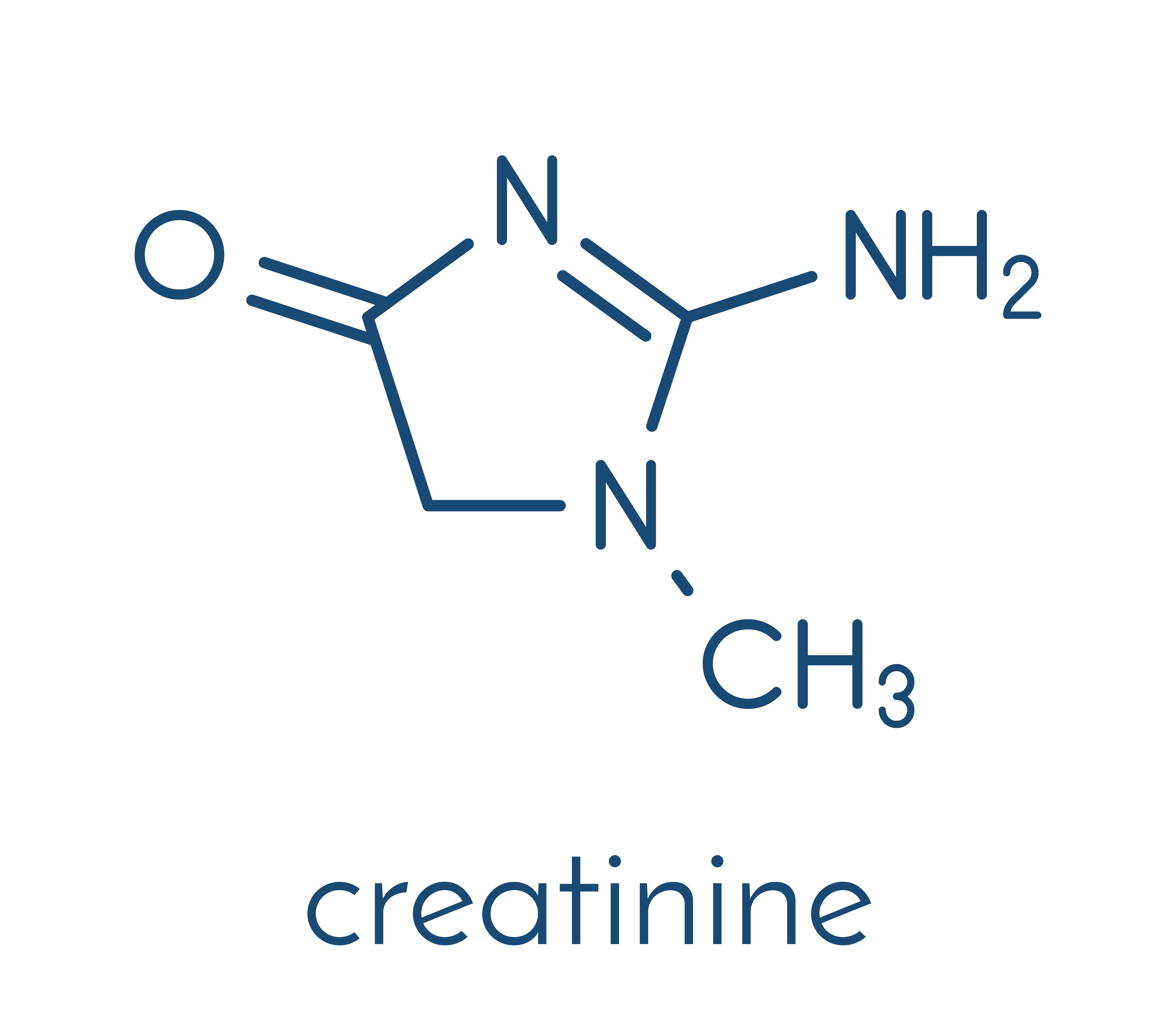
Creatine and creatine kinase - are those things the same?
Those are not the same, but fortunately in biochemistry, if something has similar names, then it's certain that those two things are related.
Creatine kinase is responsible for increasing the ratio of conversion of the creatine to phosphocreatine (a compound, which is responsible for ATP regeneration).
So, creatine kinase doesn't seems too bad right? So why its elevated level is a sign of trouble inside our organism?
That's simple. When there's "something bad happenning" inside our organism, it's mainly related to tissues damages. To repair them, body needs energy. And our energy needs is covered by ATP. To regenerate ATP, we need phosphocreatine, which is created by creatine kinase use. So, the more damage need to be repaired, the more creatine kinase is in our blood. That is why it's one of the most important tests for any kind of troubles inside our body.
When to take creatine?
Take 5 grams of creatine any time you want, really. There's no magic at taking creatine.
But to cover this topic more concretly, if you are optimalization freak, the best time to take creatine is a half an hour to one hour after training. To simplify it - after training, your muscles are like sponge for nutrients. And in such state it's easier for them to "catch" creatine compound inside, and use its supplementation better. But bear in mind, that the difference will be practically insignificant.
Creatine load and creatine cycle - are they worth the trouble?
In short - creatine load could be an option if you are impatient. Creatine cycle is on the other hand absolute bro-science and has nothing to do with additional benefits. But we will cover both of those.
Creatine load
It's a strategy of supplementing creatine, in which the intake of creatine in first week of supplementation is significantly higher, and is more or less 20 grams a day. After the first week, the intake lower to typical amount of 5 grams a day.
Why is it a thing? The period of "creatine load" increases the ratio of saturating the muscles with creatine. After that, we are taking lower amount of creatine, to just sustain the optimal level of creatine in our organism.
However, the same result will be achieved, by just taking one portion of creatine a day in longer period of time. Some studies shows, that it takes month of stable, 5 grams a day creatine intake to reach optimal creatine level in our muscles. So if you don't hurry anywhere, there's no need to load creatine.
Creatine cycle
Creatine cycles are probably the reason, why "bro-science" term got so popular. It regards any kind of theory, which we can hear at the gym but it doesn't have any sense from the biological point of view.
And that is also the thing with creatine cycle. The basic principle is, that you have to cycle creatine intake. For example you should take it 3 weeks, 5 grams a day, with 4 week off. Why? Because your body starts to get used to creatine, and you have to take a break, to maintain creatine benefits.
Whole idea is ridiculous and contradictory with the mechanism of creatine actions. The main reason to supplement creatine is the incresses its free pool for our body to use. Stopping it's supplementation will immediately decreases it's amount in our body, crippling supplementation efficiency.
So, how this myth was created? Probably for two reasons:
- We are gaining weight at the beginning of creatine supplementation. After complete satuartion of our muscles with creatine we stop to gain weight. So, the moment we stop gaining weight, we should go off of creatine. But that's only water, not muscles. That weight doesn't really count in whole matter.
- Creatine cycle looks professional (even though it's completly wrong), and bro-science followers like to sound professional (it hides their incompetence)
Is creatine safe?
Creatine is completly safe. It's a substance, which is naturally found in our organism and it's one of the basic substances of our metabolism. What's interesting, even in the biggest plea for creatine, in terms of overloading our urine tract and nephrons is ineffective, because study cases shows that nephrons can be regenerated faster with the use of creatine.
The only real negative symptom which creatine can give is bloating, especially if you start using it. But when you get used to its supplementation - congratulations. You are supplementing probably the most important supplement on the world.
Is creatine worth using?
It definitely is. Creatine has so many benefits and so little (or rather no) contradictions, that it is worth using for nearly anyone, not only if you are physically active person. Creatine improves your nervous and cardiovascular systems' health, it acts as highly potent antioxidant, it increases your regeneration and cognitive abilities potential and many, many more. Just give creatine a try!
Is creatine steroid?
Comparing creatine to steroids is like comparing a nice, little dog with wild wolf.
Steroids are substances which directly integrates in our hormonal system, acting androgenic, or estrogenic in our organism. They have a lots of contradictions, which we have covered in some other articles. Creatine, although it have some indirect effects on hormonal system, doesn't destabilize it even a bit. There's no the withdrawal effect, HPTA blocking etc. Creatine shouldn't be ever put in one line with steroids.
Creatine comprasions - what to combine creatine with?
Creatine vs whey
Whey and creatine are two of the most universal and common. There is practically no situation, where those two wouldn't benefit your diet in one, or another way. So we surely suggest not choosing between those two, but adding both of them to your diet!
Creatine vs BCAA
Creatine and BCAA is a staple combination in pre-workout supplements. Both of those could be beneficial in terms of improving training results, especially in terms of long-lasting, low-intensity training.
Creatine vs casein
Combining creatine and caseine could be good idea for the last meal of the day. Creatine will improve muscle regeneration processes, when casein will ensure enough amino acid pool for rebuilding muscles.
Creatine and caffeine
We can oftenly find creatine alongside caffeine. But there is often a problem here. Caffeine can act as diuretic, increasing water excretion from our organism, when creatine rather increases water retention from our organism.
But don't worry. Caffeine diuretic properties are not so significant, to shatter creatine benefits. What's more, caffeine increases the ratio of creatine distribution inside our organism, so combining those two substances can be actually beneficial!
Creatine and taurine
That's one of the most commonly seen combination in creatine products. And it's worth it. Taurine improves ratio of creatine distribution throughout our body, so it can be used more effectively.
What is Creapure?
Creapure is specific form of creatine, which was founded in Germany. Right now, it's probably the surest and most reputable form of creatine monohydrate. It's completly vegan (the producer confirms it by regular clinical studies of it). In Creapure we will not find any kind of byproducts like dicyandiamide (DCD) and dihydrotriazine (DHT) and unactive creatine metabolite - creatinine.
So, if you care highly about quality, not price we suggest checking creatine products containing mainly Creapure form of creatine monohydrate, for example Creatine Monohydrate Creapure from Olimp
Creatine forms - which one to choose?
There is a ton of creatine forms on the market, and question about which one to choose is probalby the one most frequently asked when you start your creatine supplementation. We can distinguish:
- Creatine monohydrate
- Creatine malate
- Creatine hydrochloride (sometimes called creatine HCl)
- Creatine nitrate
- Creatine phosphate
- Creatine ester
- Buffered creatine monohydrate
- Creatine MagnaPower (combination of creatine and magnesium)
- Creatine gluconate
- Creatine orotate
Creatine monohydrate
Before we will talk about anything else, we have to rush to creatine monohydrate form. Creatine monohydrate is probably the biggest phenomen of dietary supplements market. Why? Because even though it's firstly found form of creatine, to this day is the most sure form of creatine. It's effective, it's cheap and it doesn't have any specific contradictions. So, if you don't know what to choose, choose creatine monohydrate and take 5 grams of it everyday. And don't listen to any mumbo-jumbo broscience - it just works! The other forms can be (but not have to be) better in terms of solubility or bioavailability but often the benefits don't keep up with the price. In terms of creatine - the more expensive the better is straight lie.
Creatine malate
Okay, so we have dealt with our main competent, creatine monohydrate. Yet creatine malate is second-to-go form of creatine. Why? Because with the benefits of basic creatine monohydrate form it offers better solubility and bioavailability with it. What's the drawback? Creatine malate supplements are often sour as hell, and it's harder to take it because of this unpleasant feeling in your mouth.
Creatine hydrochloride
Oftenly, if something is in hydrochloride form, it means its highest bioaviablity (due to chemical properties of hydrochloride salts). So, hydrochloride is "something like better creatine malate". Unfortunately using hydrochloride is oftenly related to having the most intensive reflux, which can be uncomfortable.
Creatine nitrate
Just typical creatine, with higher solubility. Technically, nitrate's part of compound, should give benefits similar to nitrogen boosters but clinical studies doesn't show such actions.
Creatine phosphate
Creatine phosphate is very similar to creatine nitrate. It's just highly soluble creatine, which potentially could give additional benefits to energy metabolism due to the phosphorous groups (which potentially could increase phosphocreatine pool), but clinical studies again doesn't confirm it.
Creatine ester
Here's something interesting. Creatine ester is actually less effective than creatine monohydrate, even though it's more expensive! Theoretically, it could allow more stable creatine supply, but due to slower metabolism, the bigger part of it is metabolised to unactive creatinine, rather than distributed throughout your body.
Buffered creatine monohydrate
Buffered creatine monohydrate is kind of strange form, and its effectivness it's not widely covered by clinical studies. Technically, the smaller part of creatine can be metabolised to creatinine, due to greater resistance to pH changes, but basing on price it's rather not worth the trouble.
Creatine MagnaPower
In simplification it's a combination of creatine and magnesium. Additional portion of magnesium is never bad, but probably basing on the price it's again not worth the trouble, and more optimal option is to buy typical monohydrate and additional magnesium supplement
Creatine gluconate
Gluconate's derivatvites are oftenly associated to very high bioavailability. And combination of creatine and gluconate shows the same tendency. Such combination gives definitely higher creatine absorption, but again... Is much bigger price really worth it, rather than taking additional gram or two of creatine monohydrate?
Creatine orotate
Here we have something more interesting. Creatine orotate is rather novelty on the market, which was rather used as nonsignificant addition to creatine stacks, rather than single ingredient. But just after an Orotine Plus from Apollo Hegemony went on the market, interest in this form is risign exponentially.
Currently, it's supposed to combine benefits of creatine and beta-alanine, due to its buffering properties. But it yet to be tested. Nontheless, customers are very satisfied after some first testes, so we will surely take a closer look at every studies related to this form!
The best creatine
If you are looking for a product with the best performance, combined with the right quality, you've come to the right place! Supplements in our list have been chosen in a non-accidental way. We took into account:
- consumers opinions
- your own feelings
- interest in the product in our store (the amount of purchase of the product)
- historic feature of companies (scandals with product quality, deviations from the warehouse)
- economic option (price-to-portion ratio)
It happened that you bought creatine and did not feel the action? - Never again!
We present the best creatine products on the market!
1. OROTINE PLUS

This is a very interesting product referring to the legendary products of Man, Clout and Orotine. In its composition has a creatine associated with orotic acid, thanks to which it has additional benefits! Orotic acid raises the level of carnosine in the muscles, which helps to influence the regulation of intracellular pH during training.
2. MZ CREATINE
The MZ product is based on the only clinically tested form of creatine. The best creatine monohydrate is produced in Germany. The Creatine Powder dietary supplement has this type of raw material with excellent purity, from suppliers confirmed by attestations.
3. GREEN MAGNITUDE

Green people appreciate many people as a "creatine stack" because there are 2 types of creatine. 2-Creatine Malate and Magnesium Creatine Chelat. The second is a very interesting combination of a creatine molecule with magnesium. In the opinion of users, this is a supplement that "works for everyone", so if you have used creatine so far you were not happy - try Green Magnitude!
4. CREA STACK
CREA STACK is also a measure classified as "creatine stacks", among many considered the best! The combination of 6 different forms of creatine gives great anabolic effects. The product works well with long reduction cycles so you can keep your strength and lose less muscle mass during reduction catabolism.
5. CM3

Creatine malate - everyone has heard about it, many have used it. It is a great alternative to creatine monohydrate. Maybe it is not the best creatine on the market, but it is at the forefront of products, and among creatine malate is number one!



