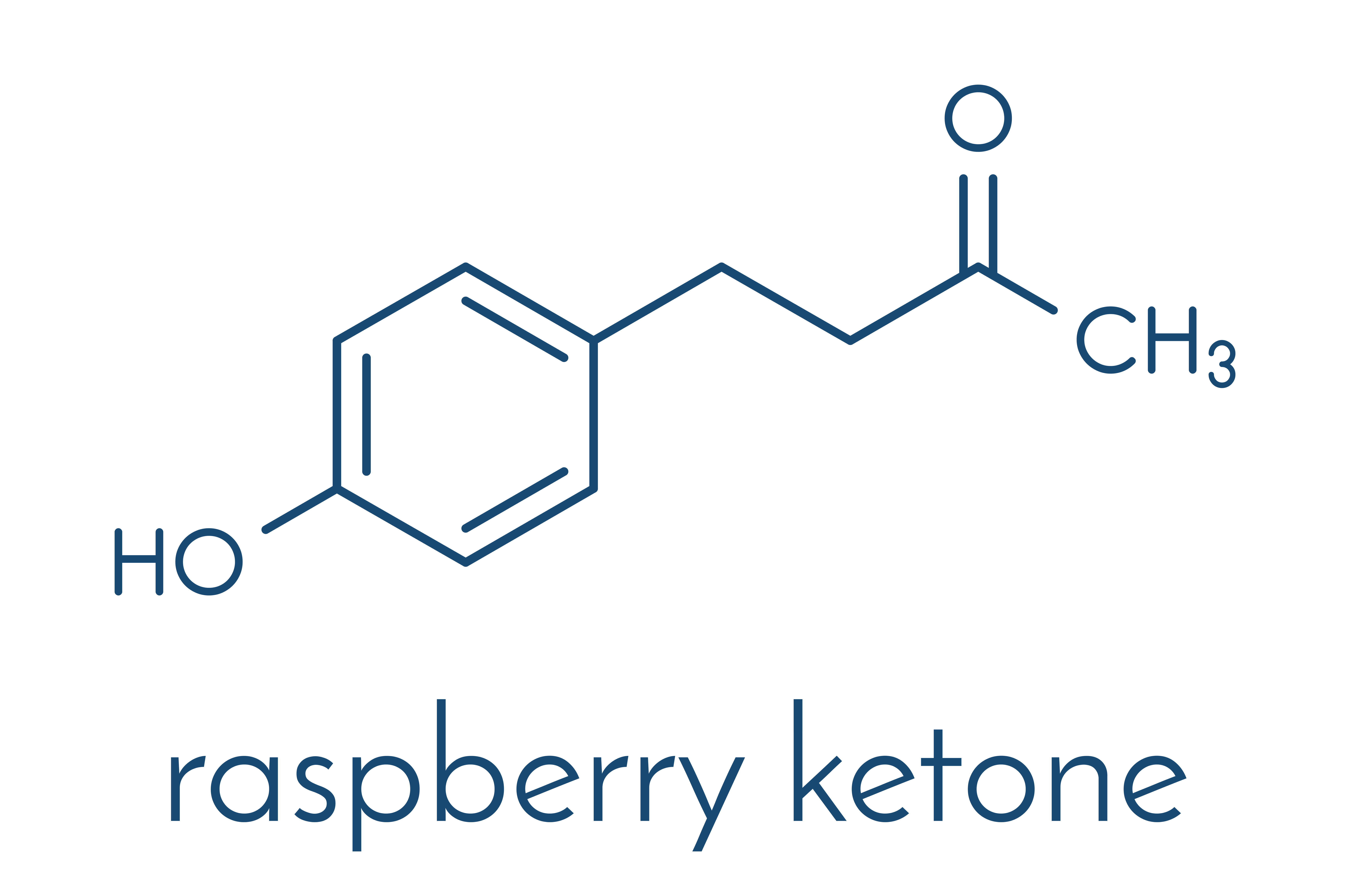
Raspberries contain ca. 200 particles, which are responsible for their taste. One of them are raspberry ketones, which were distinguished and appreciated by food producers a long time ago, due to their strong smell. Raspberry ketones are used to produce sweets, soap and candles as well as other food and care products. Recently, researchers once again paid attention to raspberry ketones, however, this time due to their potential of facilitating weight loss.
Raspberry ketones - origin
Raspberry ketones may be found in cranberries, blackberries and red raspberries or a less popular variety - Rosaceae Rubus idaeus L. Red raspberries come from Europe, North Africa and Central Asia. They have essential nutrients, including beta-carotene and vitamins A, E and C. In fruits there are only trace amounts of raspberry ketones, therefore food with berries often takes advantage of raspberry ketones produced in laboratories.
In the year 2010 researchers noticed that raspberry ketones have similar molecular structure as capsaicin, which is a substance responsible for the spiciness of chili peppers. Preliminary studies also suggested that capsaicin prevents weight gain. In the light of these results, scientists carried out research on mice and human tissues in order to check weather raspberry ketones also influence body mass reduction.
Do raspberry ketones work?
“Currently there are no trustworthy studies on the influence of raspberry ketone on the health of humans”, said Catherine Ulbricht, senior pharmacist in the Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston and co-founder of the organization Natural Standard Research Collaboration, which analyzes the activity of herbs and supplements.
Raspberry ketones for fat loss
Only a few of preliminary studies were carried out in order to test the influence of raspberry ketone on weight loss, but none of them was carried out on people. Studies on mice and human cells proved, however, the potential of this ingredient. As a result of the study on mice fed by a high-fat diet, published in 2005 in the gazette Life Sciences, it was concluded that raspberry ketone prevented the increase of mass in the liver and limited the gain of abdominal fat (fat on the belly), which surrounds organs.
It was proven in another study that these ketones accelerated the breakdown of lipids (fat molecules) in fatty cells. According to the article published in 2010 in the magazine Planta Medica, ketones stimulated fat cells to produce a larger amount of adiponectin. Lower content of adiponectin in the organism appears more often among obese people and people with diabetes type 2.
A study from 2016 presented at the conference of experimental biology proved that mice, who were applied a high-fat diet put on weight less, since they were fed at the same time with raspberry ketones and ellagic acid, another particle found in raspberries. Studies also proved that raspberry ketone changed the expression of genes in the liver in the way which turned out to be effective for the health of the mouse.
However, in the study from 2017, carried out by scientists in Denmark, it was suggested that raspberry ketone on its own is not able to decrease the level of adipose tissue in the organism. In this study, published in the magazine Food & Function, the researchers concluded that mice on a high-fat diet and raspberry ketones achieved lower weight in comparison to mice, which were not administered raspberry ketone. However, mice fed with ketone did not consume as much food as mice, which were not fed with this particle. In the end, the scientists concluded that raspberry ketone does not decrease the level of fat more than a low-calorie diet.
Initial studies also proved that raspberry ketone - used directly on skin - may help in fighting the signs of aging. According to the study carried out in 2008 and published in Growth Hormone & IGF Research, the improvement of skin elasticity and hair growth during five months was noticed in 15 subjects.
Studies od mice and cells growing in laboratory vessels often inspire more research. In order to obtain trustworthy results, doctors need to carry out many tests on people. These tests, in order to be considered trustworthy, need to be carried out on many participants, at different ages and of different sex. In general, Human Performance Resource Center of the American Department of Defence concluded that the evidence of weight loss with the help of raspberry ketone are “insufficient”. Natural Standard Research Collaboration classified raspberry ketone as “C” when it comes to the amount and quality of proofs supporting health benefits of this ketone.

Are raspberry ketones safe?
In the 60s, U.S. Food and Drug Administration classified raspberry ketones as a supplement “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS). However, the status of GRAS is granted with the assumption that a person consumes less than 2 milligrams of raspberry ketone per day. The majority of weight loss supplements contain much more.
Raspberry ketone hasn’t been well-researched in the concentrations used in supplements - from 50 to 250 milligrams per portion. There were some side-effects identified, resulting from their application.
“Raspberry ketone may decrease the level of sugar in blood and decrease the risk of bleeding” - said Ulbricht. People who take drugs for diabetes should be strictly monitored by doctors. Raspberry ketone may also cause changes in adipose tissue and body weight, changes in inflammations, palpitations and convulsions. Ketone may also interact with drugs, such as the ones that regulate pulse, cholesterol and hormones.
“Currently there are no trustworthy information regarding the safety of use of raspberry ketones in people”
said Ulbricht.
In the study from 2015, published in the Journal Toxicology and Pharmacology, researchers from Denmark examined potential effects of using ketone by people. Their discoveries suggest that raspberry ketone may have potential side effects and toxicity in case of very high doses. “Potential toxicity needs to be tested in further experimental research”, said the researchers.






One Comment