Glucose is a monosaccharide which is a basic energy material for cells. Its proper concentration in the blood determines all life processes. Glucose is obtained from food or produced in the body through glycogenolysis or gluconeogenesis. It is distributed to the body cells with the blood flow.
The correct level of blood sugar
The correct fasting blood sugar level is one of the basic indicators of good health. Disorders in this matter may indicate the development of serious diseases, such as diabetes. The fasting blood glucose concentration should be between 70 and 99 mg/dL.
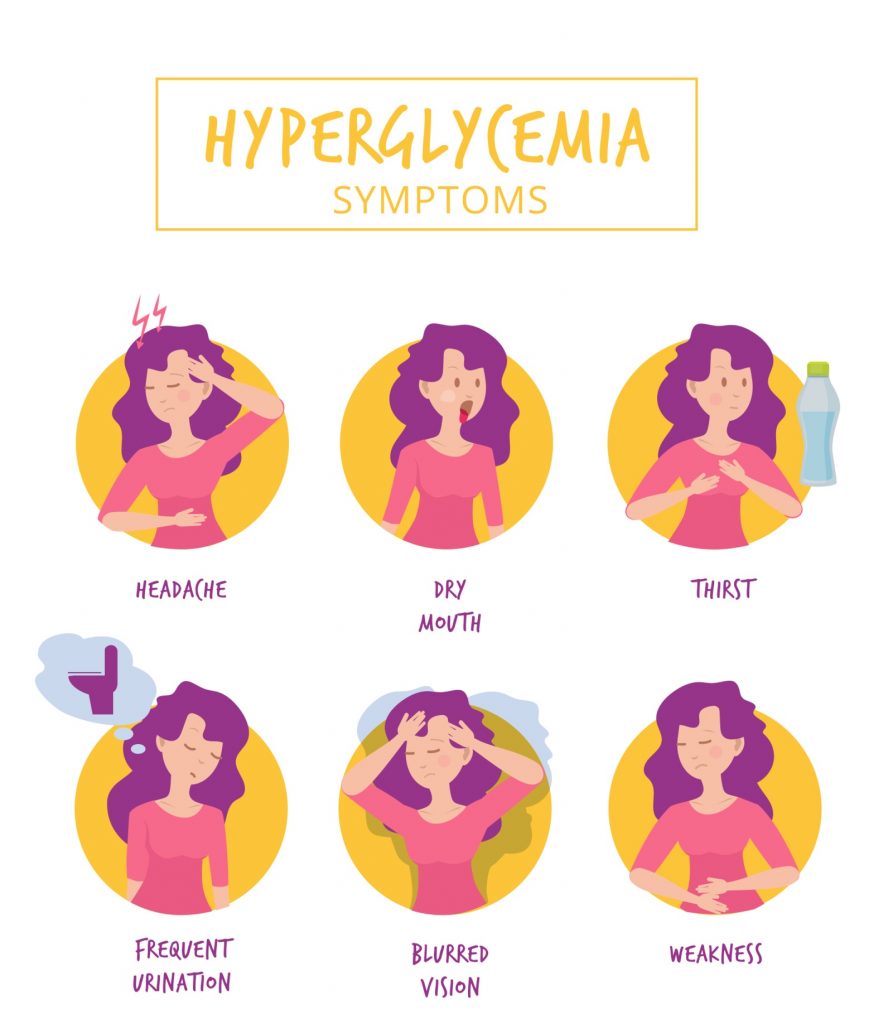
A condition in which sugar exceeds the assumed standards is called hyperglycemia. Its occurrence may suggest the development of pre-diabetes or diabetes mellitus. Persistent hyperglycaemia is a very dangerous phenomenon.
Too high blood sugar level and health
A prolonged increase in blood sugar levels makes the body mobilize the pancreas to produce the insulin necessary for the cells to use glucose as an energy source.
This causes a high secretory load on this body, which may lead to a decrease in its capacity in the future. In addition, high insulin concentrations are a factor that promotes the growth of body fat. This hormone increases the synthesis of fatty acids and triglycerides that fuel fat cells. Glycemic disorders are often associated with excessive body weight.
Repeated hyperglycaemia leads to serious health complications such as reduced immunity, worse wound healing, visual disturbances or damage to peripheral nerves. Through a proper diet and often also through appropriate pharmacotherapy, blood sugar levels can be stabilized.
What reduces blood sugar levels?
The diet of people with elevated blood sugar should be based on low-processed products. An important element of it is appropriate, i.e. low and medium glycemic index and glycemic load of used ingredients. The index and glycemic load is the rate at which blood glucose levels increase after consumption of a given product. Therefore, the diet should be composed based on:
- vegetables - especially those with low carbohydrate content such as green pepper, tomato, green cucumber, cauliflower, zucchini, spinach, chives, lettuce, cabbage, broccoli, radish, chicory
- grain products rich in fibre - wholemeal pasta, brown rice, oatmeal, rye, wholemeal bread
- products rich in protein - meats such as turkey, lean beef, veal, fish including oily seafood, dairy products, eggs
- healthy sources of fats such as - nuts, seeds, linseed, rapeseed oil
- the adequate amount of unsweetened liquids - with a high proportion of mineral water, this helps to control glycemic levels
High blood sugar - what to avoid?
An equally important part of a diet to reduce blood sugar levels is to avoid products such as:
- sugar
- sweets
- sweetened drinks
- alcohol
- sweetened dairy
- fast food products
- products made of white flour, e.g. white bread
It is also worth to start controlling the amount of consumed fruit and fruit juices. Despite the high nutritional value associated with polyphenols, vitamins, minerals and fibre, they also contain monosaccharides, which when consumed in excess will adversely affect the state of glycemia.
Diet for hyperglycemia - principles
- eating 4 -5 meals per day
- adding raw vegetables to every meal - especially those with low carbohydrate content
- introduction of regular physical activity - improves tissue sensitivity to insulin, reduces blood glucose levels
- drink 2 litres of unsweetened drinks daily with high participation of still mineral water, green tea and herbal teas
- consume fish and legumes once a week
An important part of the diet is to properly combine products to reduce the glycemic index of a meal. It is worth choosing products rich in fibre and combining them with products containing protein and healthy fats. Through appropriate combinations, we can slow down the digestion process and reduce the rate at which blood glucose increases.






